
Microbial culture
We are always ready to consult with companies and research institutions that can work together with us to create new products by utilizing our knowledge of research and development technologies related to the cultivation of microorganisms.
Index
Ⅰ.Culture of useful microorganisms
1-1 Classification of useful microorganisms and fermented foods
1-2 Useful bacteria and their relationship to human development and health, and industrial applications
1-3 Our Fermentation Technology and Facilities
1-4 Our Characteristics of Microorganism Culture Technology
Ⅱ. On useful microorganisms and the functionality of fermented foods
2-1 Value-added improvement of functional ingredients
2-2 Utilization of unused resources
2-3 Exploration of new functionalities
2-4 Collaboration with universities and efforts up to industrialization
2-5 Features related to functional research
Ⅰ. Culture of useful microorganisms
1.Classification of useful microorganisms and fermented foods
Useful microorganisms are divided into prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes include Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria that make yogurt, Actinomycetes that make medicines such as streptomycin, and Bacillus subtilis that makes natto. On the other hand, eukaryotes, which are the same as humans, include yeast and koji mold that make sake, miso, soy sauce, and wine, mushrooms called basidiomycetes, fungi such as blue cheese and Penicillium that makes penicillin, a pharmaceutical product, and algae that perform photosynthesis like plants.
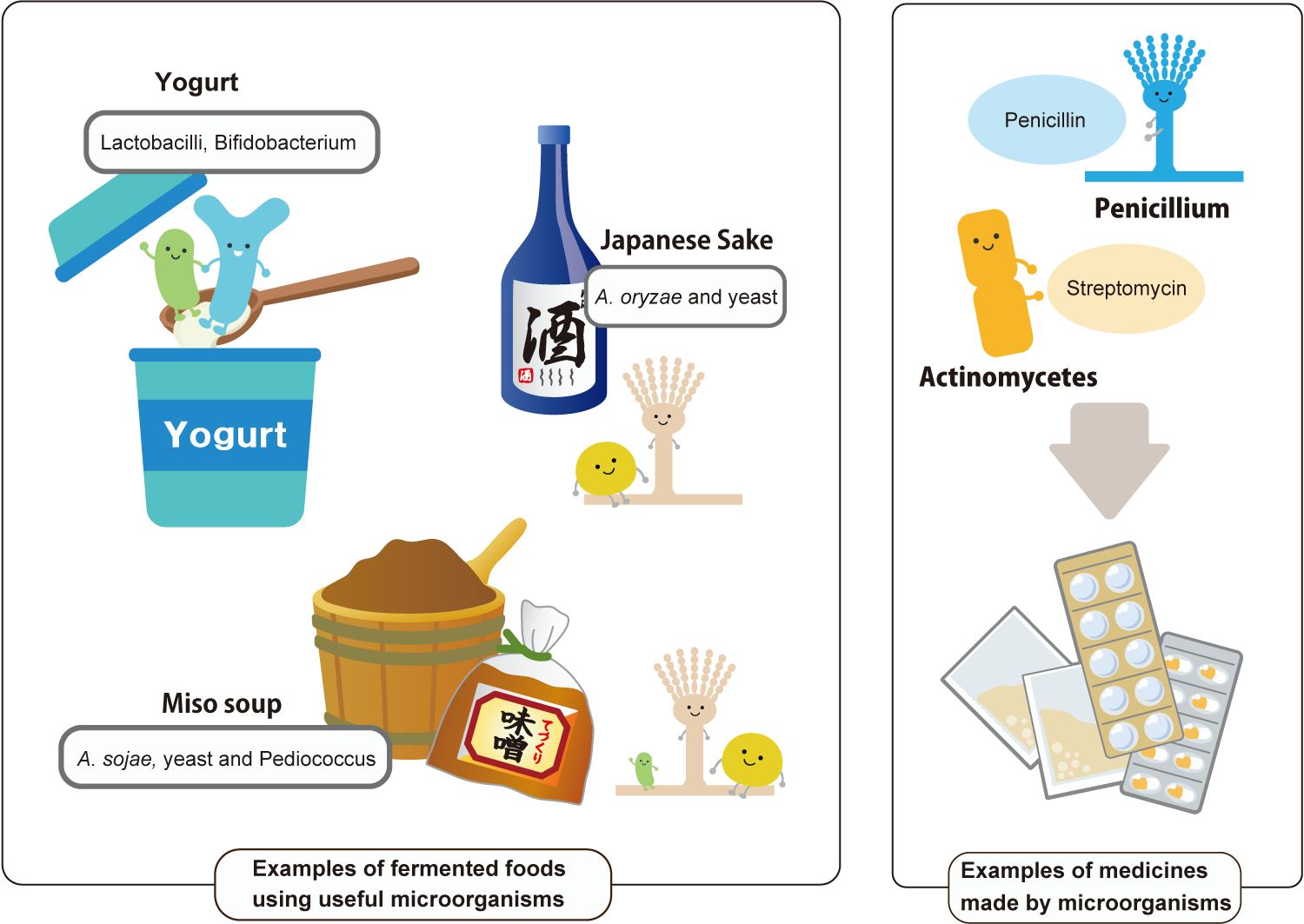
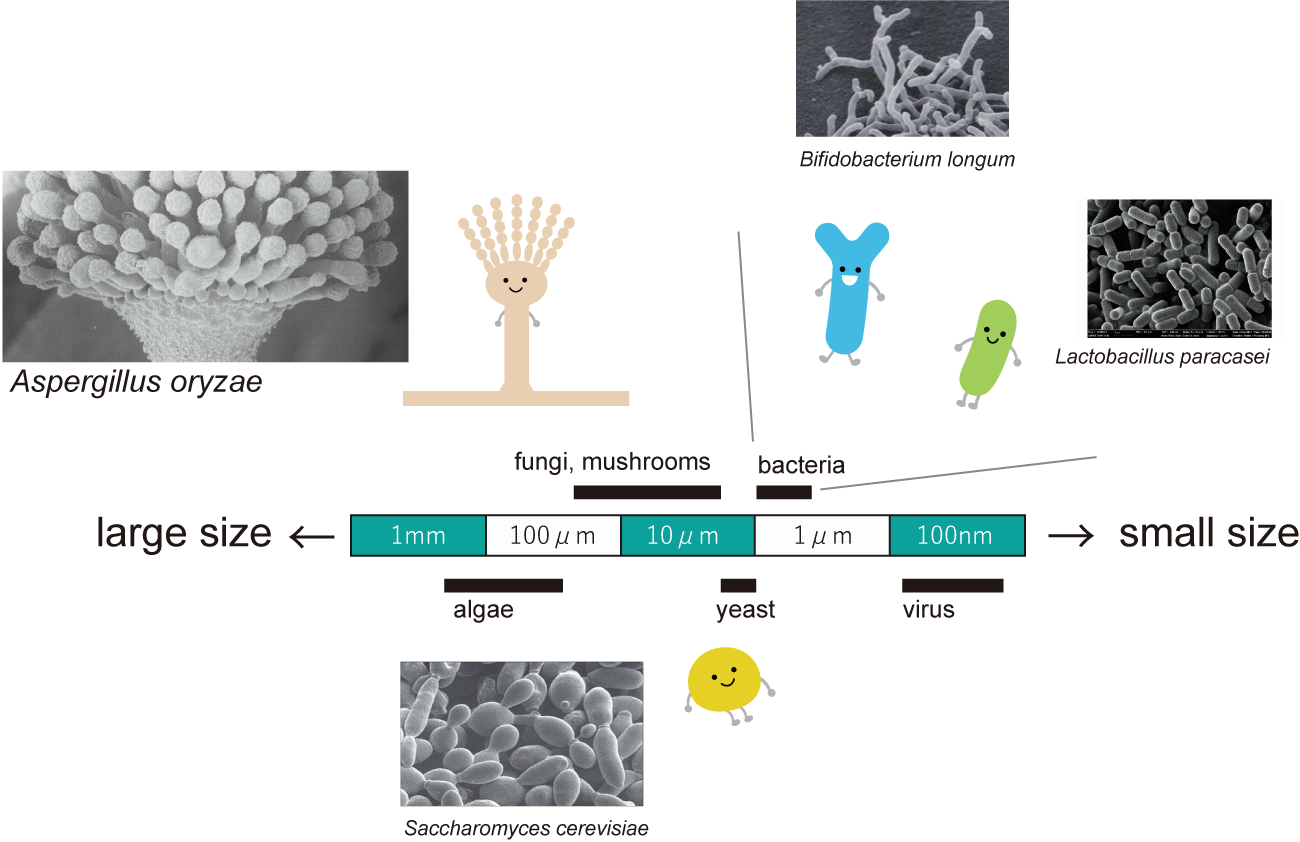
Bacteria are broadly classified into Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria based on the presence or absence of cell walls, and aerobic, facultative anaerobic or anaerobic bacteria based on their ability to aerobic metabolism. Fermented foods that are beneficial to the human body are mainly produced by utilizing these bacteria and fungi. “Fermentation” and “spoilage” both refer to the process by which bacteria metabolize food components. The term “fermentation” refers to bacterial metabolism that suppresses the growth of putrefactive bacteria and improves food preservation, or produces substances useful to the human body, while “spoilage” refers to bacterial metabolism that produces toxins harmful to the human body.
2.Useful bacteria and their relationship to human development and health, and industrial applications
The bacteria that reside in the intestinal tract of humans are called intestinal bacteria, and have been thought to be involved only in the digestion of human. It has also been shown to be an important factor in the maintenance of health, including the prevention of lifestyle-related diseases and various illnesses.
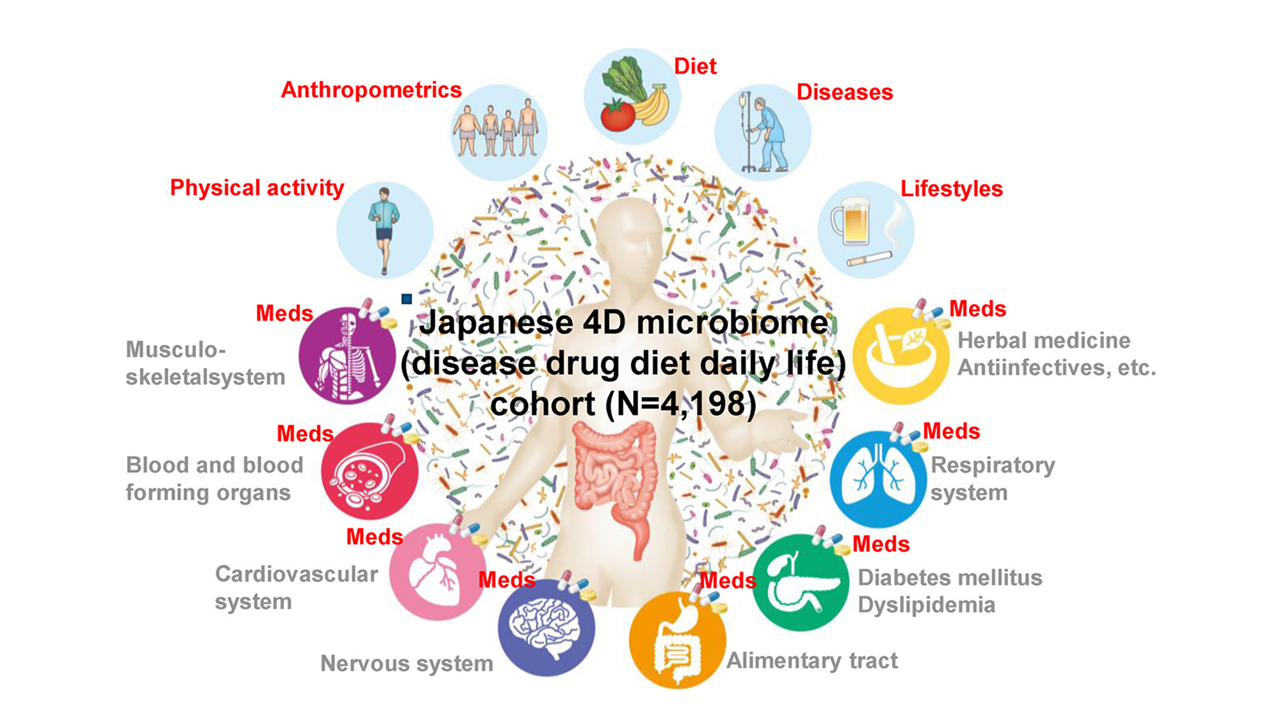
(Gastroenterology 2022;163:1038–1052)
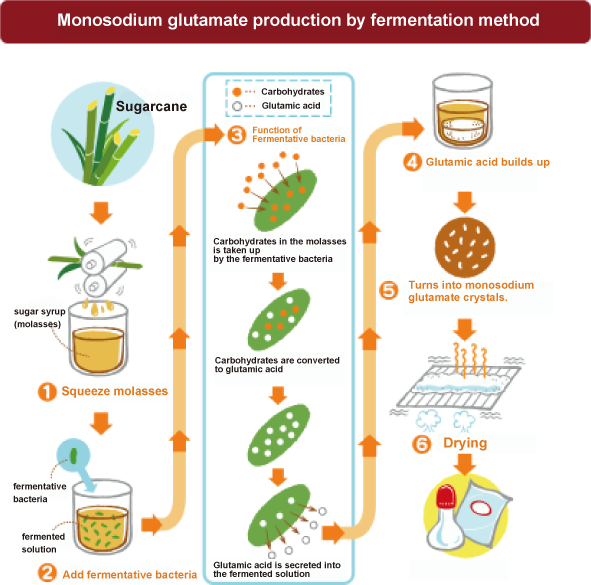
Bacteria are also used in industrial production to obtain large amounts of certain desired metabolites by utilizing the metabolism of useful microorganisms. A typical example of industrial use is the industrial production of monosodium glutamate, a substance used in umami seasonings, using sugarcane and the Corynebacterium glutamicum to safely produce large quantities. This is called the fermentation method. Recent research has also developed a growth-independent bioprocess that, unlike the conventional fermentation method, immobilizes useful bacteria and utilizes only their metabolic functions.
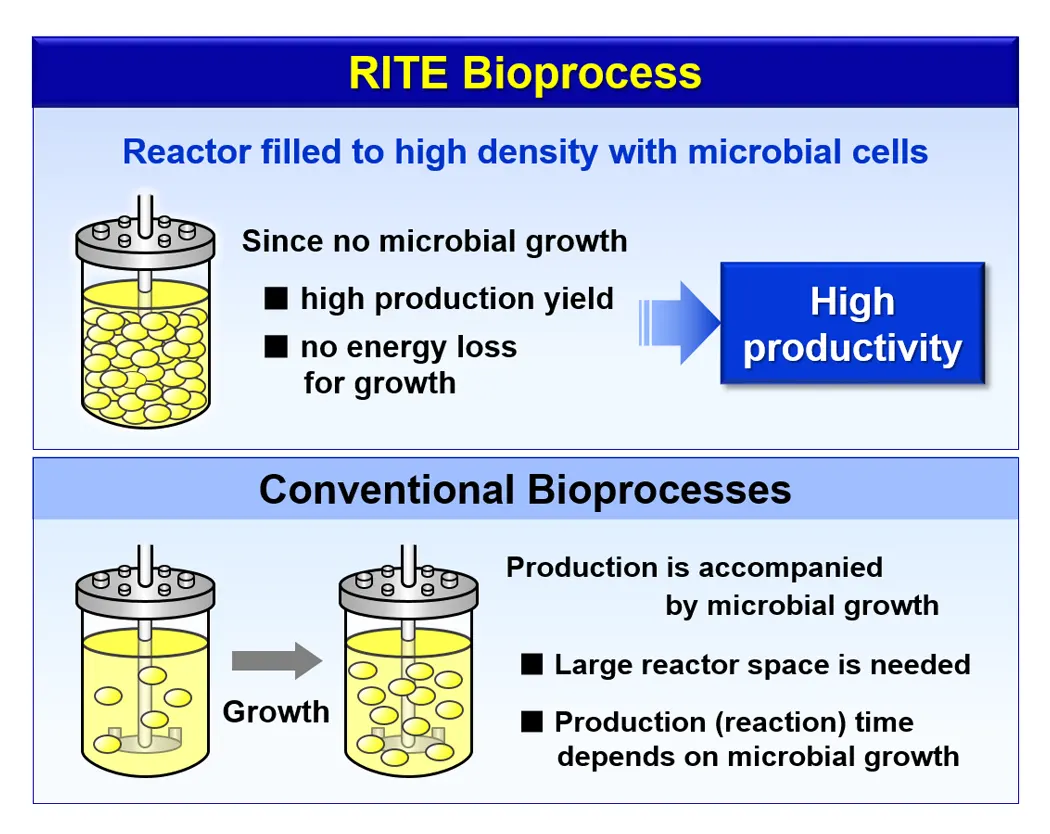
3.Our cultivation techniques and equipment
Yaegaki Biotechnology keeps and researches many original microorganism libraries isolated from the natural world, and we call a wide variety of unutilized useful microorganisms “seeds”. The unique technology is characterized by its ability to study the characteristics of each bacterium.
In the cultivation of seeds, we study the characteristics of each bacterium, and our unique technology is characterized by the study of cultivation conditions for more efficient propagation of the bacterium and obtaining more of the desired metabolites.
We are able to perform everything from the examination of culture conditions in a laboratory scale of a few liters to the scale-up to a large scale culture tank in our own laboratory and factory facilities, and our dedicated researchers will work with you seamlessly from planning to actual production for each project.
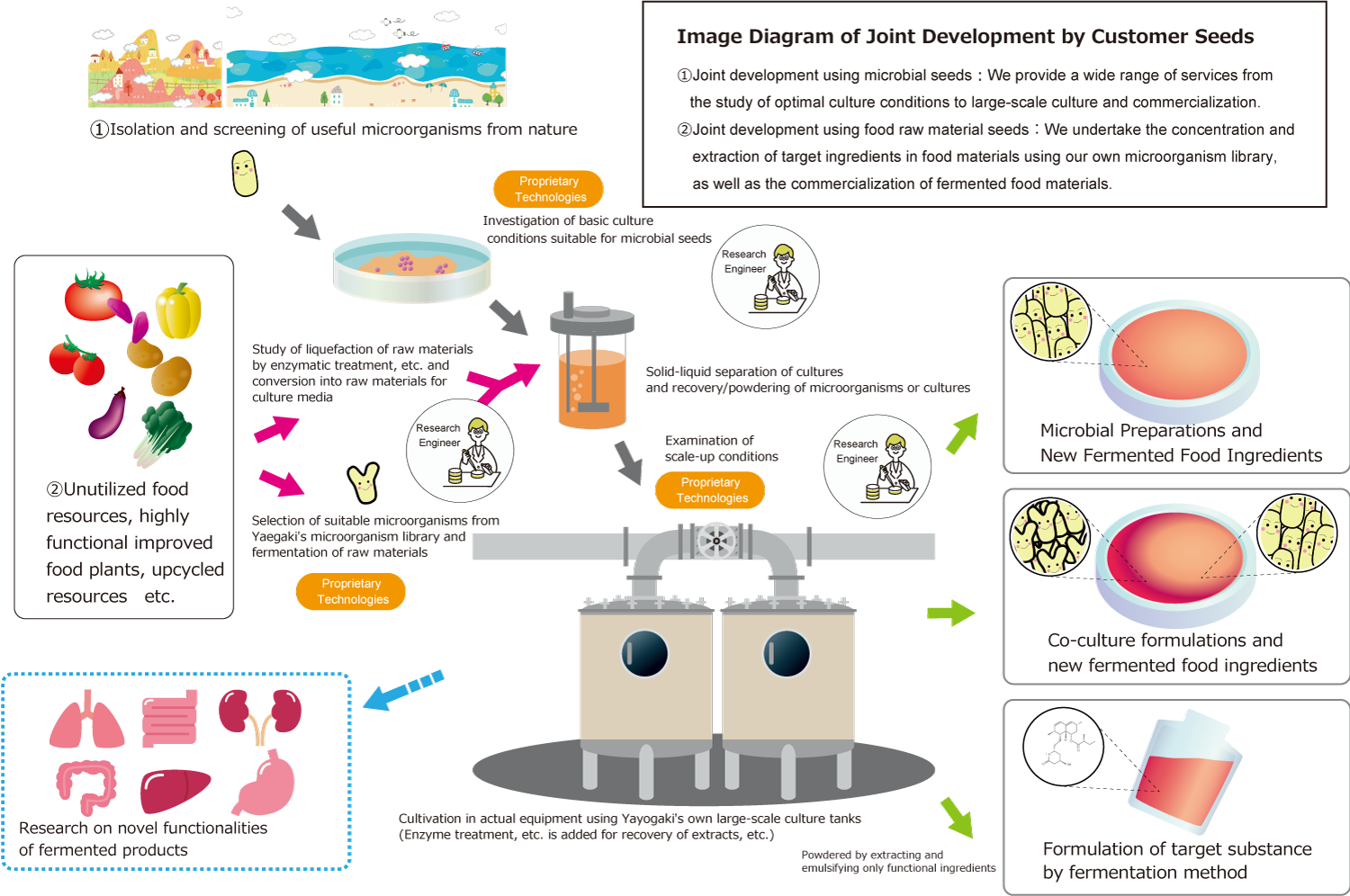
4.Our characteristics of Microorganism Culture Technology
●We have experience and technology in culturing a wide range of microorganisms from bacteria to fungi and algae, and have knowledge of their industrial production (mass cultivation) (*Some species such as Bacillus subtilis, certain types of biotic anaerobic bacteria and genetically modified microorganisms cannot be manufactured.)
●We can also consult with you on the selection of bacteria and culture media materials (e.g., to ferment certain types of plants with useful microorganisms) according to the purpose of food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and other products.
●Co-culture (simultaneous fermentation of multiple bacteria, such as the parallel multiple fermentation of koji mold and yeast in sake) and multi-step culture (separation of a portion of the culture product of a microorganism to be used as a medium for the next microorganism in a multi-step fermentation process):You can also consult our product examples: PROFIBER®🔗, PROFINE®🔗
●We have several large culture tanks and a stable production system. We also offer batch culture (adding culture medium and not removing the fermentation liquid until fermentation is complete), flow culture (adding culture medium ingredients little by little to increase the growth rate of the bacteria), and continuous culture (adding culture medium and removing the fermented product continuously to keep the culture medium in a steady state). Please contact us for more information.
●We can separate and purify the bacteria and fermentation liquid from the culture tank, and we can powder the bacteria and culture medium together at our partner factory.

Ⅱ. On useful microorganisms and the functionality of fermented foods
Yaegaki Biotechnology also conducts research on the functionality of fermented foods and metabolites of useful microorganisms. We not only produce microorganisms, their metabolites, and raw materials for fermented foods, but also identify and quantify functional ingredients, and provide consultation on product standardization.
1.Value-added improvement of functional ingredients
By fermenting functional ingredients contained in plants and foods with the power of microorganisms, we can convert them into ingredients with enhanced functionality and improved absorption. We can consult with you on the selection of suitable bacterial seeds, establishment of culture methods, and experimental planning for human intervention tests with a view to complying with functional food labeling.
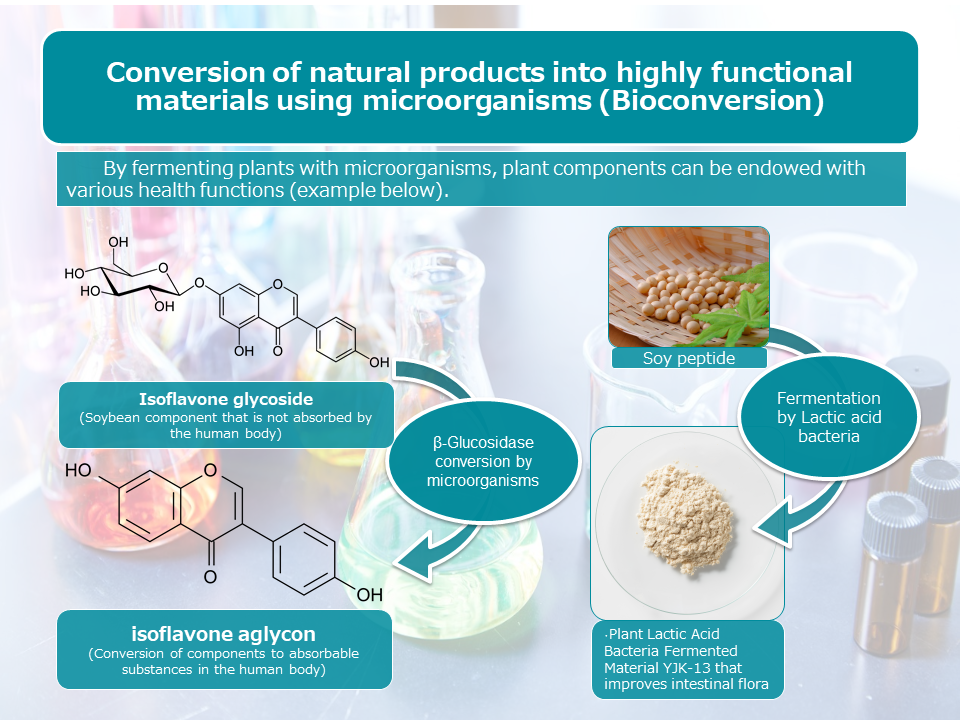
2.Utilization of unused resources
Due to the increase in global population, there is a growing need for the effective utilization of raw material residues from food factories, which until now have been discarded and not used, and for the development of alternative products to animal products. For this reason, new food processing and preservation technologies called “food tech” are being developed. Traditional fermented foods, which we are used to eating, must be called as the primitive food tech, and their processability and preservation properties have been improved by the power of microorganisms. Fermentation technology using new useful microorganisms will play an important role in solving global issues such as the utilization of unused resources and the development of alternative animal products, and this is an area in which we are particularly interested in collaboration.
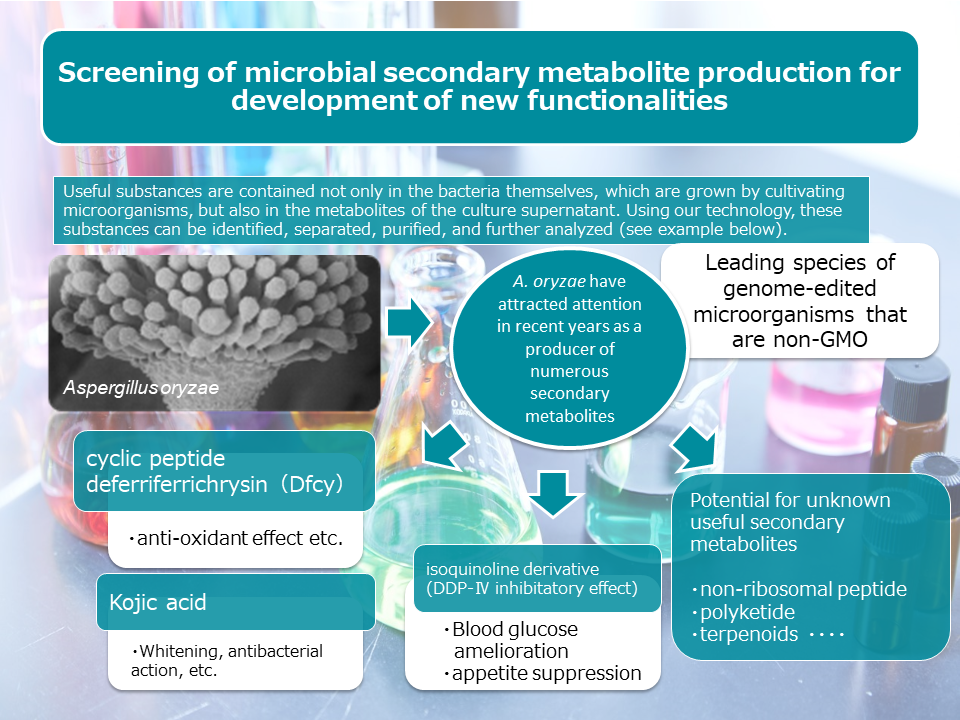
3.Exploration of new functionalities
We search for new functionalities of fermented foods, beneficial components of useful microorganisms, and their metabolites for human healthcare by various medical and biological approaches, and also conduct various safety tests. In addition, we will consult with you not only from an academic perspective, but also from a marketing perspective to design themes such as what consumers need now and what the future market potential is.
4.Collaboration with universities and efforts up to industrialization
For more efficient research and development, we collaborate with various research institutes to accelerate the speed of industrialization. As an example, the Biocommunity Kansai (BiocK), which aims to “bring together the bio-knowledge of Kansai,” the core of the bio-industry in Japan, plans to conduct research collaboration aimed at innovating culture technology to accelerate “biomanufacturing” and to improve efficiency up to social implementation.
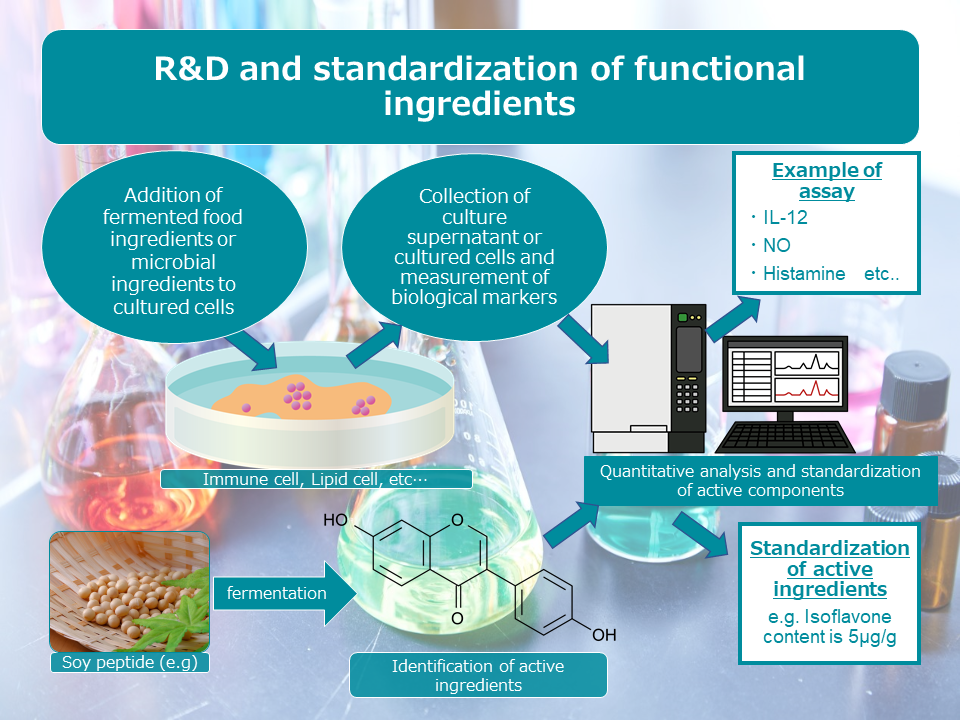
5.Features related to functional research
In order to enhance the functionality of food products through fermentation, we can select suitable microbial seeds, establish culture methods, and study their functionality.
We also provide consultation on the development of fermentation products that can contribute to the SDGs by using useful microorganisms, such as the utilization of unutilized resources.
In addition to medical and biological approaches to examine functionality, we can also consult with you on improving functionality by concentrating and emulsifying useful components of fermentation products by utilizing our technologies for extracting and separating and refining components from plants in the development of natural pigment products over many years.