Plant Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermented Material YJK-13
Plant Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermented Material YJK-13 is made by Yaegaki’s original plant-derived lactic acid bacterium JK-13 strain, having excellent digestibility and absorption. It provides not only nutritional and functional values of soybean peptides, but also shows promising immunostimulatory activity and intestinal lactic acid bacteria regulation effects.
General Information
| Functions | ・Antioxidant effect ・Immunostimulatory effect ・Intestinal improvement |
|---|---|
| Form | Powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Form of delivery | 500g×10 bags |
| Recommended intake | 0.1~1.0g/day |
※The information on this page is intended for people in the health food industry, and does not claim any effects or efficacy of the product.
Table of Contents
1. Development Story
1-1 Isolation of lactic acid bacterium JK-13 strain and its effect on immunity
1-2 Improving effect on stress-induced immune balance
1-3 Plant Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermented Material YJK-13 Production path and nutritional components
2. Clinical data
2-1 Antioxidant Effect
2-2 Endurance improving effect
2-3 Immunostimulatory effects
2-4 Intestinal regulation
1.Development Story
- 1-1 Isolation of lactic acid bacterium JK-13 strain and its effect on immunity
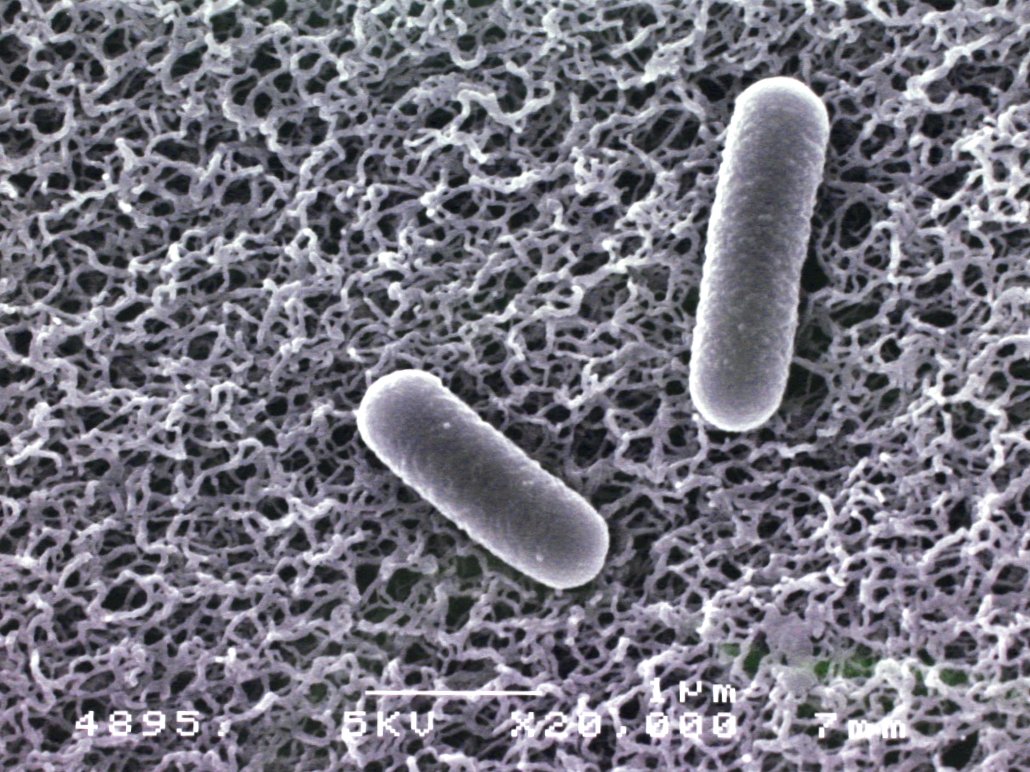
Lactobacillus plantarum JK-13 is a unique lactic acid bacteria strain owned by Yaegaki Biotechnology. It is a plant-derived lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional Japanese pickled vegetables. It shows a strong ability to activate human immune cells when taken even in small amounts. For example, 1 g of YJK-13 material contains 10 billion Lactobacillus plantarum JK-13 (heat-treated dead bacteria) which is equivalent to 100 g of yoghurt.
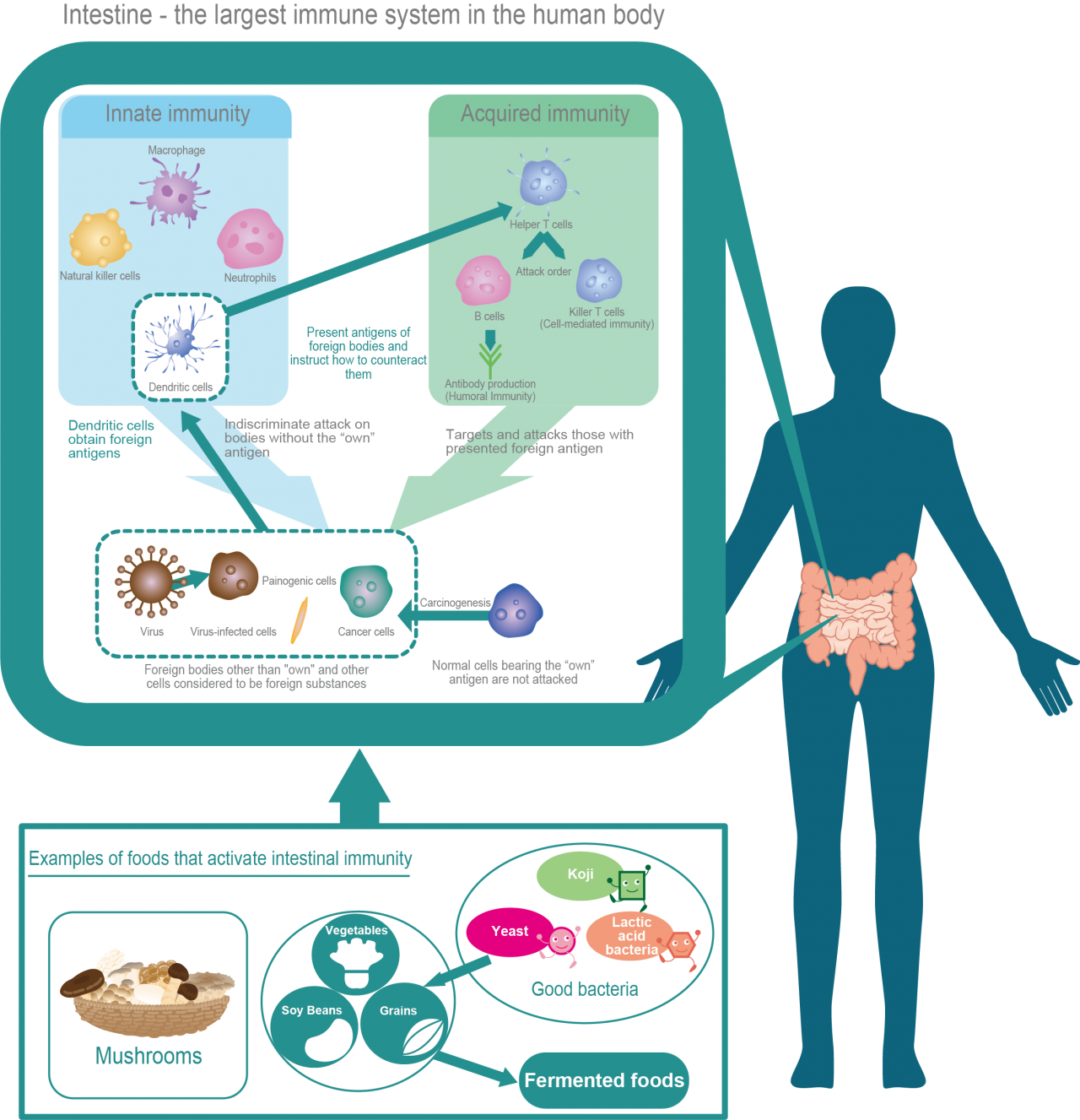
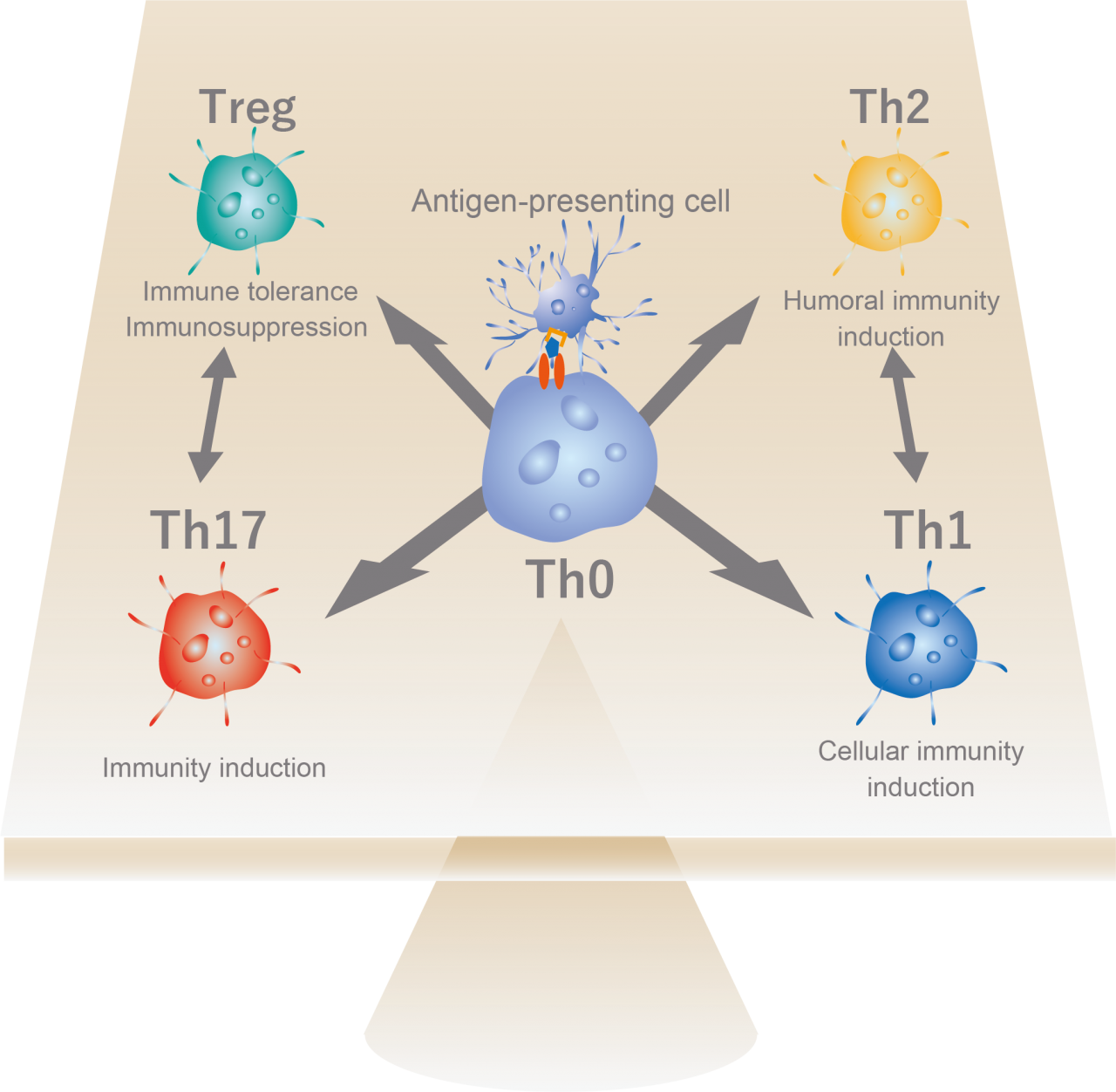
The human immune system cells can be divided into two main categories: innate immune cells, which attack everything “except themselves”, and acquired immune cells, which attack only their intended targets. In particular, it is now attracting attention that efficiently activating the innate immune cells of the intestinal tract with so-called good bacteria and functional ingredients contained in various foods also activates acquired immunity, leading to general immune system improvement throughout the body. Various lactic acid bacteria components are presented by antigen-presenting cells to naive T cells (Th0), which are known to balance the differentiation of helper T cells, and restore the balance from the allergy type (Th2-dominant type) common in humans to the cellular immunity-inducing Th1-dominant type.
- 1-2 Improving effect on stress-induced immune balance
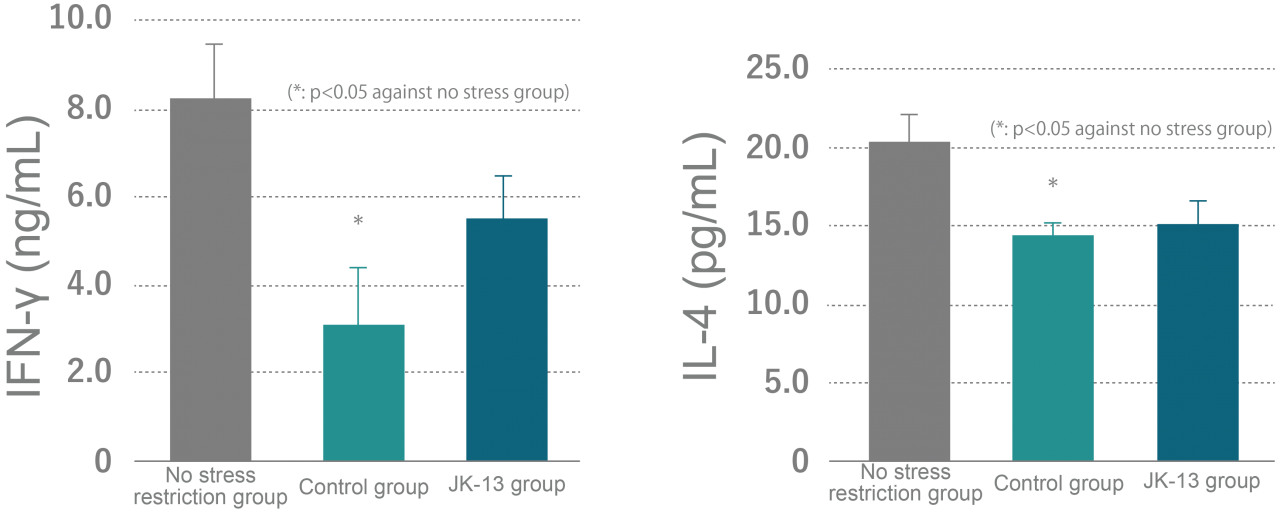
| Subjects | Balb/c mice |
| Samples | Lactic acid bacteria JK-13 heat-killed cells or the same amount of placebo (2 mg/day oral administration) |
| Period | 14 days |
| Trial outline | Mice were orally administered the test sample from day 0 to day 14 of the study. To induce stress subjects were restrained in 50 mL tubes for 2.5 h daily from day 8 to day 14 of the study. On day 14 mice spleen cells were removed and adjusted to 5 x 108 cells/mL, treated with ConA (concanavalin A) and cultured for 20 hours, after which cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-4) were measured from the culture supernatant. |
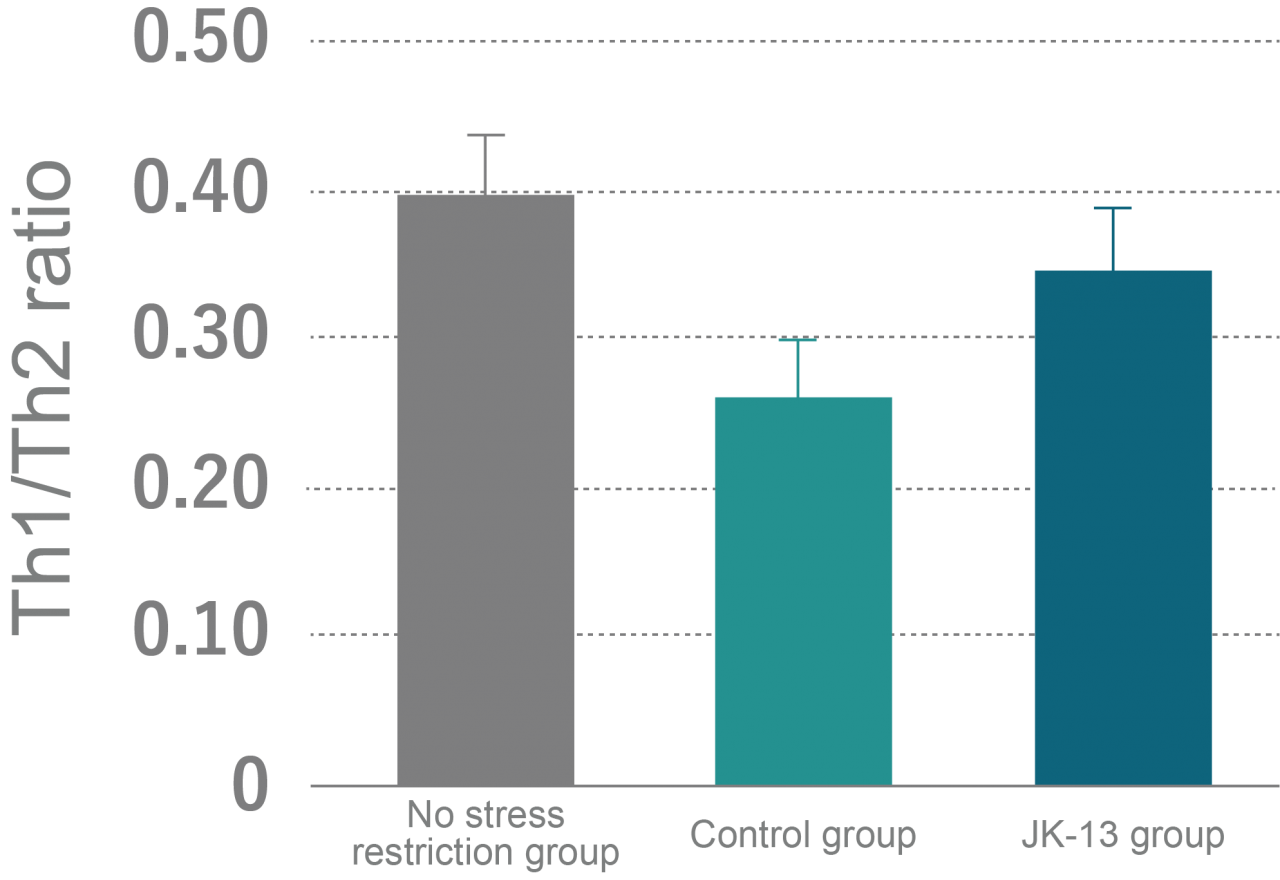
It is known, both academically and experientially, that stress reduces immunity. In modern society people are restricted from moving freely, which can easily lead to a state of ‘restraint stress’ and decline of the immune system. In this experiment mice were confined in a narrow tube to induce chronic restraint stress, and Lactobacillus JK-13 role on the immune balance change was investigated. The test results showed that the Th1/Th2 balance was disrupted by chronic restraint stress, which was then improved by the intake of Lactobacillus JK-13.
- 1-3 Plant Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermented Material YJK-13 Production path and nutritional components
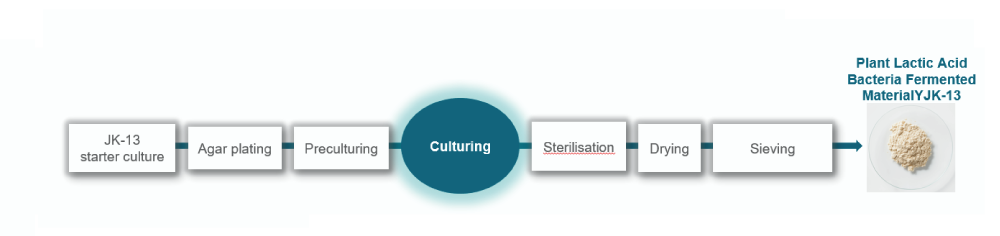
Plant Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermented Material YJK-13 (hereafter YJK-13) is a food ingredient made by liquid cultivation of lactic acid bacteria strain JK-13 (Lactobacillus plantarum JK-13). During production only soya is used as raw material with addition of dextrin. After cultivation stage the culture is sterilized, dried and powdered to the final product state.
Protein content of YJK-13 is more than 70%, which is similar to the nutritional content of soya beans. In recent years, this type of lacto-peptides has been attracting attention as a functional ingredient that works even in minute quantities. A unique characteristic of YJK-13 is high lactic acid Lactobacillus plantarum JK-13 bacteria content of 10 billion cells/g.
| Nutritional components(/100g) | YJK-13 |
|---|---|
| Proteins | 76.7g |
| Fats | 0.06g |
| Minerals | 4.36g |
| Carbohydrates | 10.5g |
| Energy | 359kcal |
| Dietary fiber | 4.68g |
2. Clinical data
- 2-1 Antioxidant Effect
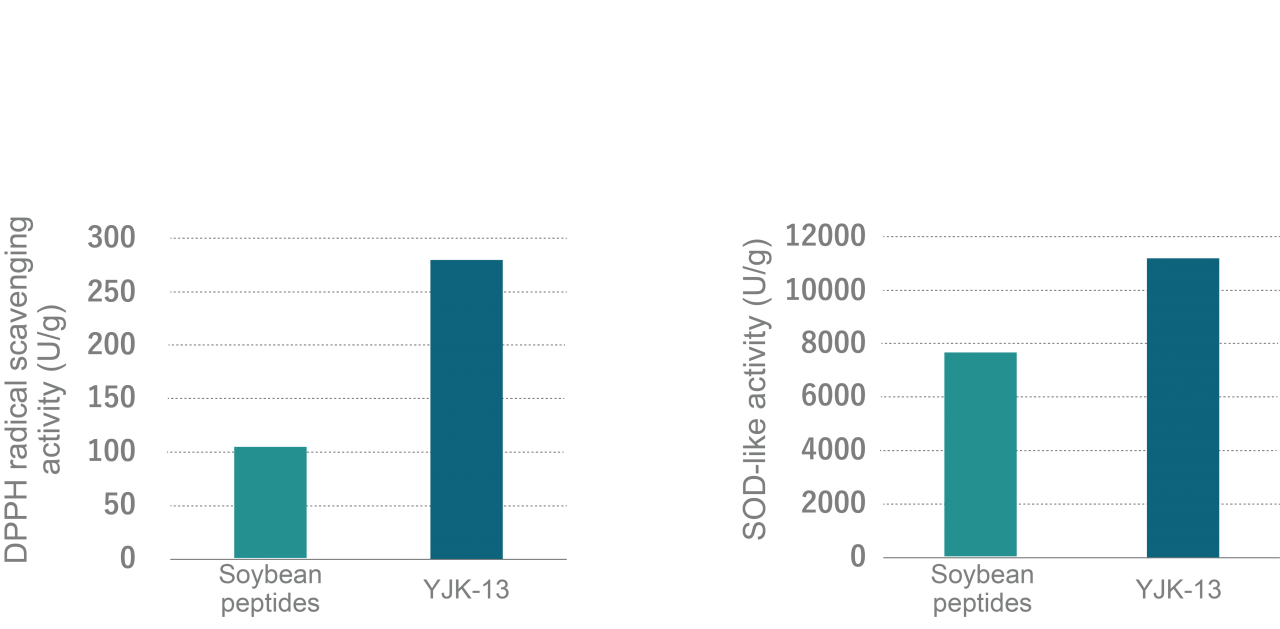
Soya proteins are known to have antioxidant properties when they are converted into peptides by degrading enzymes. Various types of peroxides can cause damage to human body, however scanning experiments with them might be difficult due to their short life time. In order to investigate antioxidant activity of YJK-13 a relatively stable DPPH radical was used.
Trial outline
in vitro samples were adjusted to 2% with ion-exchange water, stirred well, and centrifuged (15 000 rpm, 3 min). Then, DPPH radical scavenging activity of the centrifugal supernatant was measured. Superoxide (O2–) – a typical example of reactive oxygen species, its scavenging capacity (SOD-like activity) was also investigated.
Trial results
Strong radical scavenging and SOD-like antioxidant activity of YJK-13 was observed.
- 2-2 Endurance improving effect
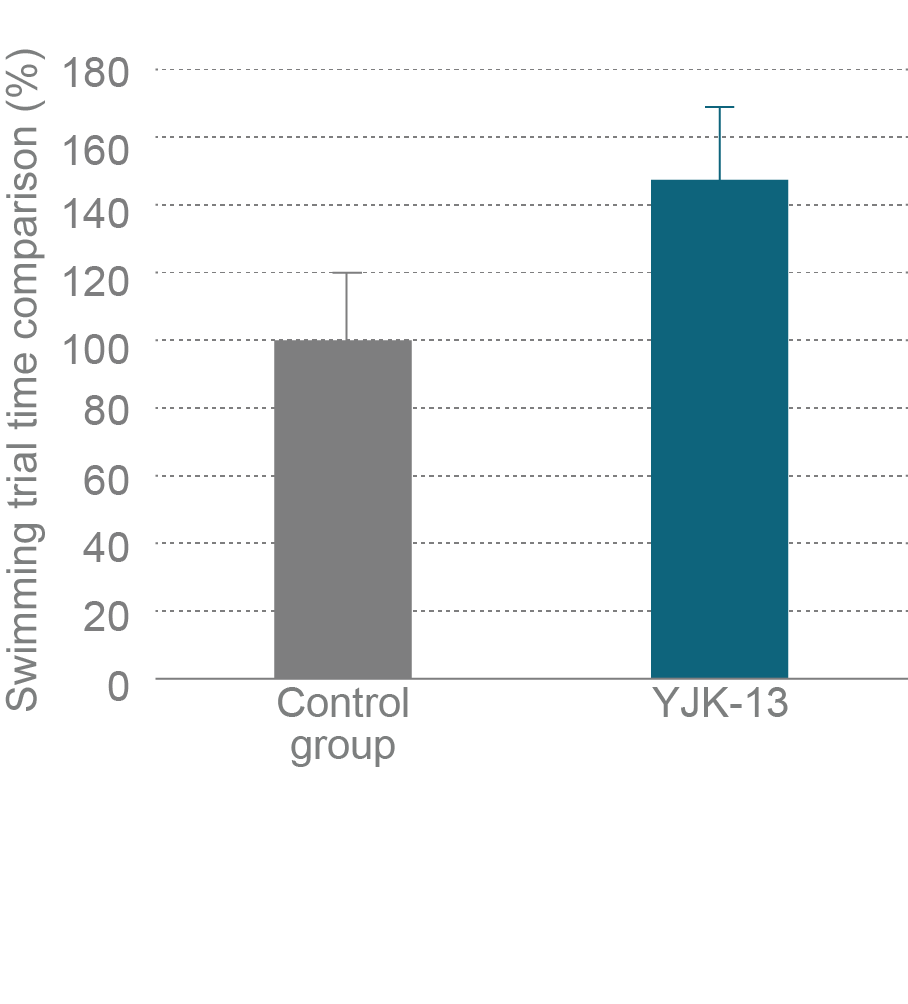
Trial outline
YJK-13 amino acid protein composition is high (approximately 16%) in branched-chain amino acids (BCAA: valine, leucine and isoleucine) . Branched-chain amino acids, also called endurance-related amino acids, are reported to be useful for endurance improving together with antioxidant peptides. Therefore, the effect of YJK-13 on endurance was investigated in mice.
| Subjects | 7-week-old female ICR mice (n=12) |
| Samples | YJK-13 group; control group was given same dose of water (1.0 g/kg B.W) |
| Period | 2 weeks of consecutive administration |
| Trial outline | Mice were orally administrated with samples 30 minutes before swimming and then allowed to swim with a 7% of body weight attached to the tail. Swimming time was measured as the time until subjects could not swim anymore. |
Trial results
An trend for increased swimming time in the YJK-13-treated group was shown compared to the control group. This suggests that antioxidant peptides and BCAAs contained in YJK-13 help to improve endurance.
- 2-3 Immunostimulatory effects
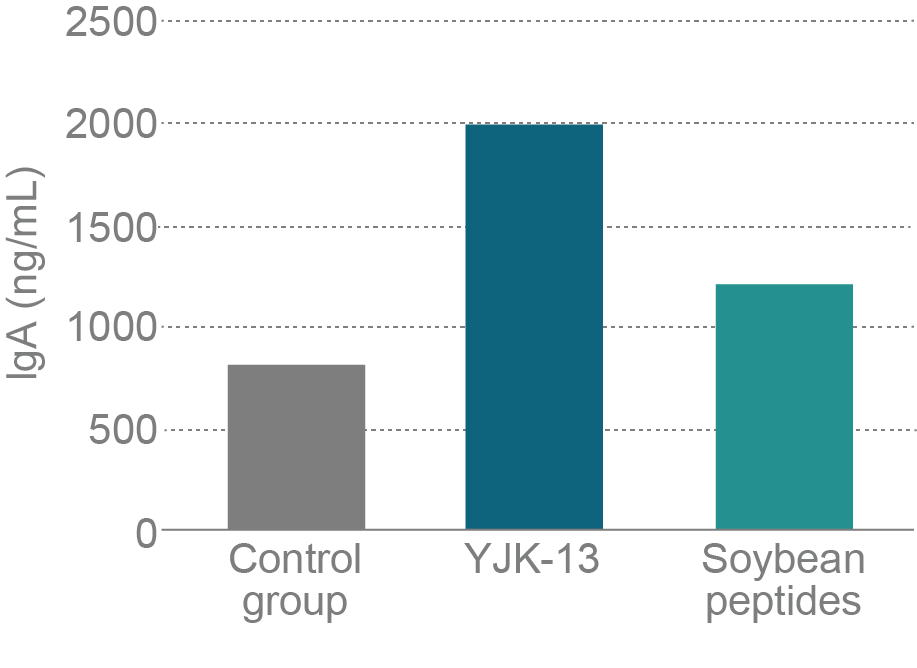
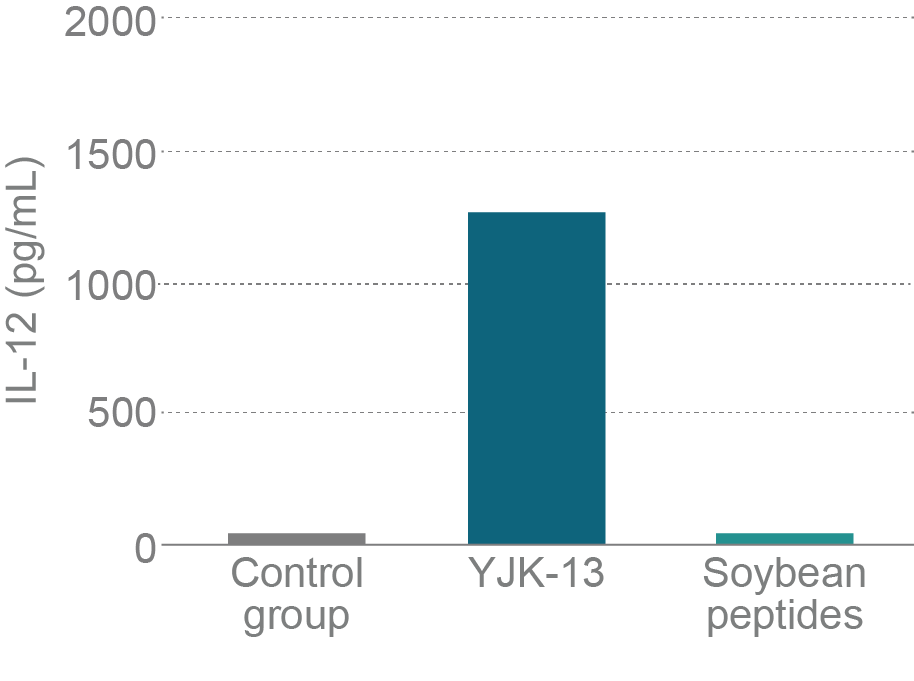
Trial outline
Lactic acid bacteria are known for activating Type I helper T cells (Th1), which stimulate mucosal and cellular immunity, and also for improving the immune balance that causes invasion of foreign substances through mucous membranes and allergies. Activity of YJK-13 on Th1 cells was investigated using cultured cells (5×106 cells/mL of mice spleen cells or Peyer’s patch cells).
| Cultured cells | Peyer’s patch from Balb/c mice (mucosal immunoassay) and splenocytes (cellular immunoassay) |
| Samples | YJK-13, soya peptide, water (100 µg/mL) |
| Period | After sample addition Peyer’s patches were cultured for 5 days and spleen cells for 24 hours |
| Trial outline | Samples were added to the respective mice cell culture media. IgA and IL-12 were measured at the end of the incubation period. |
Trial results
Compared to soy peptides, YJK-13 showed a higher ability to induce IgA production in Peyer’s patch cells and IL-12 production in splenocytes. This confirms that YJK-13 is useful for stimulating mucosal and cellular immunity.
- 2-4 Intestinal regulation
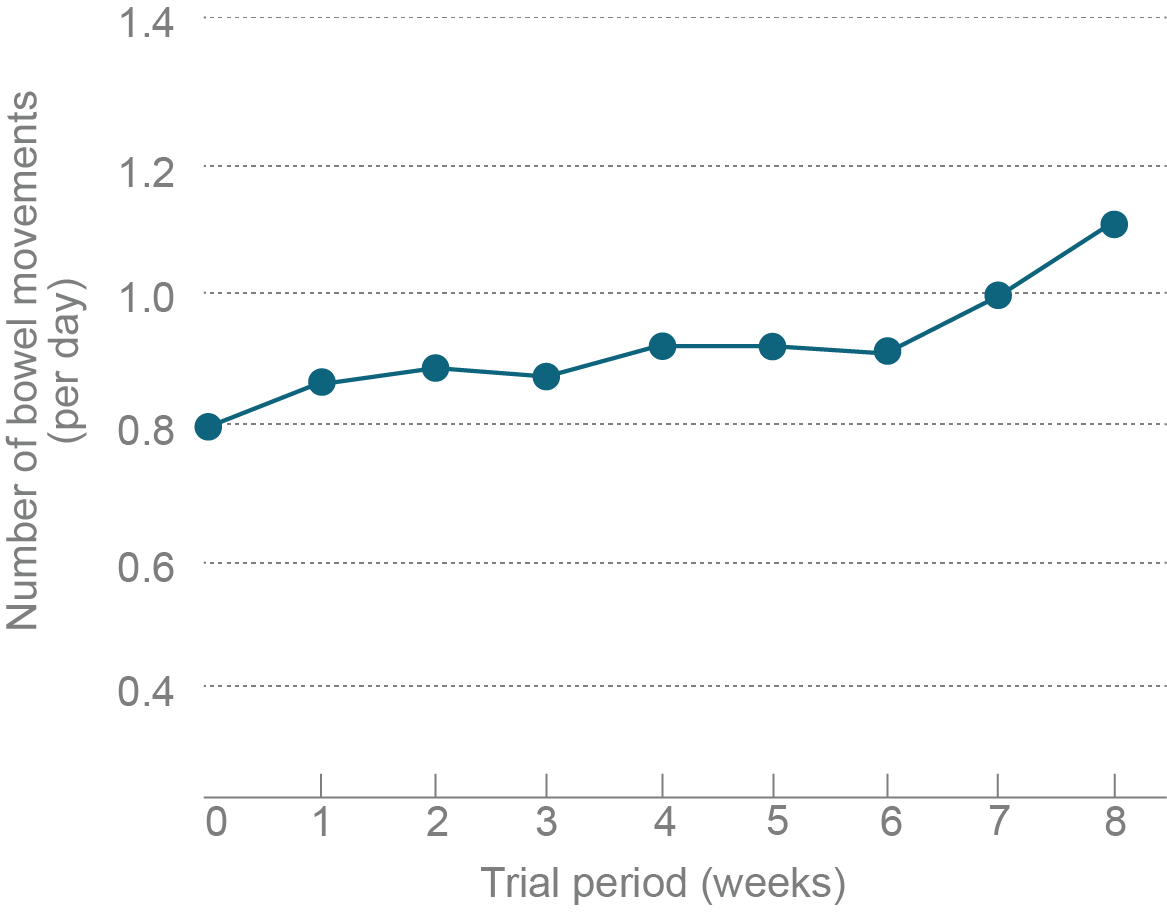
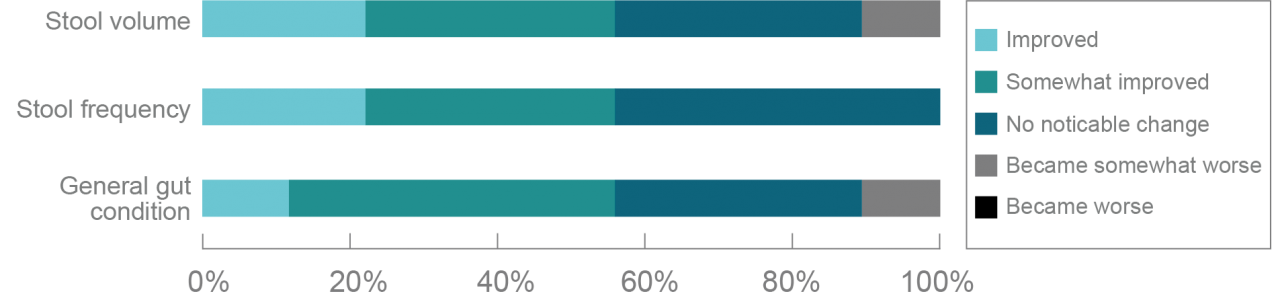
Trial outline
To investigate the bowel regulating effects of YJK-13, healthy volunteers with a tendency to constipation were administered with YJK-13 for 8 weeks.
| Subjects | Healthy adult women with constipation symptoms (n=9) |
| Samples | YJK-13 600mg/day |
| Perios | 8 weeks |
| Trial outline | YJK-13 was consumed daily during the study period. After which a post-test questionnaire was carried out. |
Trial results
YJK-13 intake significantly increased bowel movement frequency from week 7 of the study, and a trend towards better bowel movements in comparison to control group was observed in more than 50% of subjects.
