Agaricus Mycelium FM
Agaricus Mycelium FM is a functional material made by liquid cultivation and powdering of Agaricus mushroom mycelium. It is abundant in β-glucan, which is shows to have anti-tumour and immunostimulating effects.
General Information
| Functions | Immunostimulatory effect |
|---|---|
| Form | Powder |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water |
| Content | More than 25% of β-glucan |
| Form of delivery | 1 kg (Product name: Agaricus mycelium FM(S)) 10 kg |
※The information on this page is intended for people in the health food industry, and does not claim any effects or efficacy of the product.
Table of Contents
1.Development Story
1-1 Immune Cell Activation and Agaricus β-glucan Content
1-2 Production Path and Nutritional Components
2. Added Functionality
2-1 Innate Immune Activation (Tumor Cell Suppression)
2-2 Acqured Immune Activation (Increased Lymphocyte Proliferative)
2-3 Lymphocyte Proliferation Effect in Mice
1.Development Story
- 1-1 Immune Cell Activation and Agaricus β-glucan Content

Agaricus – mushroom species in the genus Halatetes that have long been referred in academic literature as Agaricus blazei Murill. Our company has been conducting research on functional materials for many years, paying special attention to Agaricus mushroom due to its immune cells activating function. The main research was focused on a fruit body of the mushroom, however, in 1999 it was found that the mushroom root-like structure called mycelium has higher β-glucan contents (the main component that activates immune cells) and the research was switched towards the mycelium. As a result we were able to successfully increase β-glucan contents up to three times that of the pure mycelium by our unique fermentation technology. Since then, the research has been continued to obtain evidence of potential functions added to the mushroom mycelium by means of fermentation.
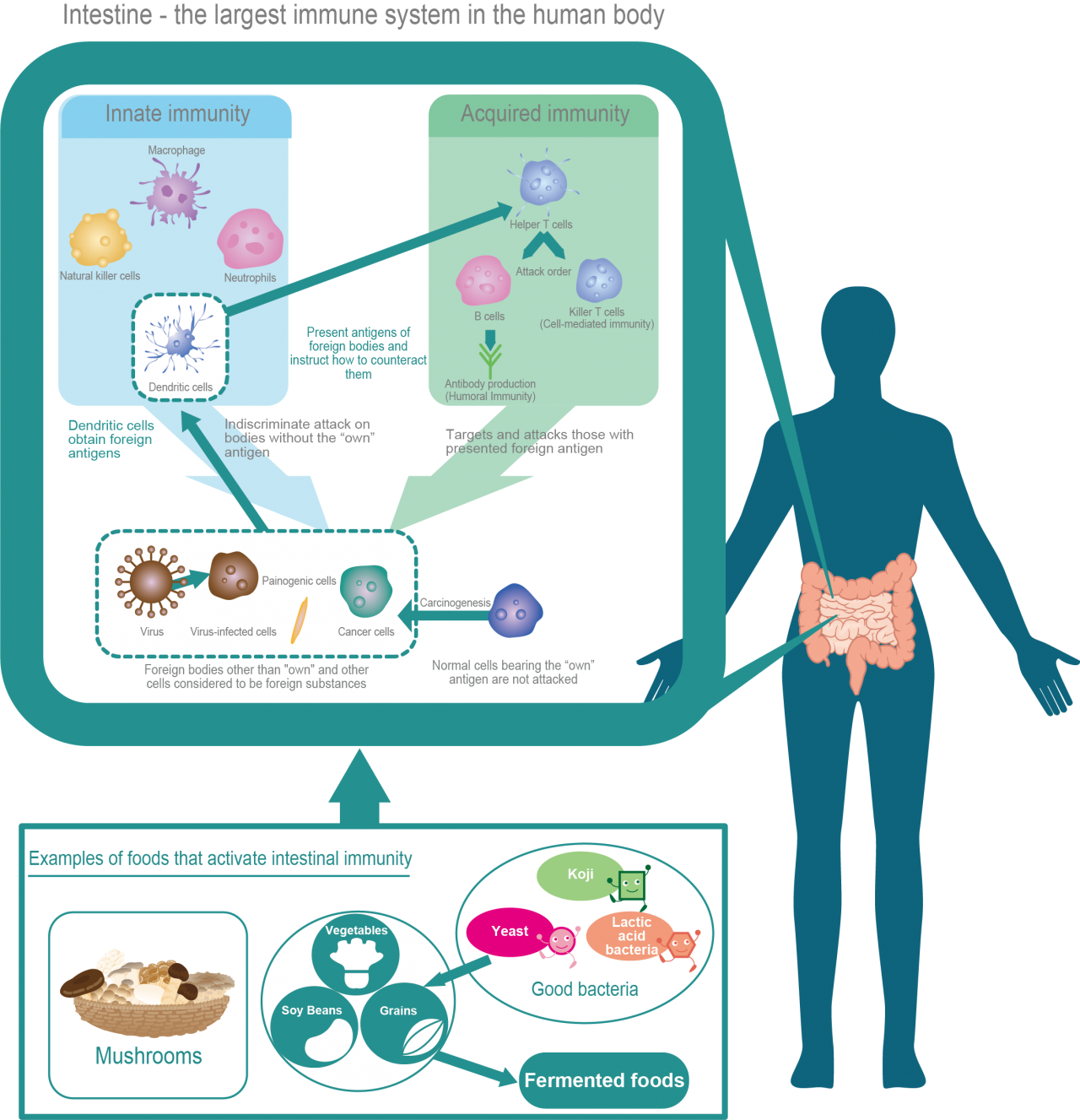
The human immune system cells can be divided into two main categories: innate immune cells, which attack everything “except themselves”, and acquired immune cells, which attack only their intended targets. Representative examples of innate immune cells include macrophages (phagocytes), which attack foreign substances; NK (natural killer) cells, which attack cancer cells and virus-infected cells that have become cancerous and are regarded as foreign substances, and other granulocytes. Acquired immunity, on the other hand, plays a major role in the immunity of humans and other higher animals and is represented by lymphocytes (T cells and B cells). Recent research has shown that 60% of human immune cells are concentrated in the intestinal tract, and it is now attracting attention that efficiently activating immune cells in the intestinal tract with so-called beneficial bacteria and functional ingredients contained in various foods can help maintain a healthy immune system throughout the body
- 1-2 Production Path and Nutritional Components
| Ingredients(/100 g) | Agaricus Fruit Body | Agaricus Mycelium FM |
|---|---|---|
| Proteins | 37.2g | 24.3g |
| Fats | 2.4g | 4.6g |
| Minerals | 6.0g | 3.4g |
| Sugars | 27.2g | 4.8g |
| Energy | 281kcal | 158kcal |
| Dietary fiber | 18.4g | 54.9g |
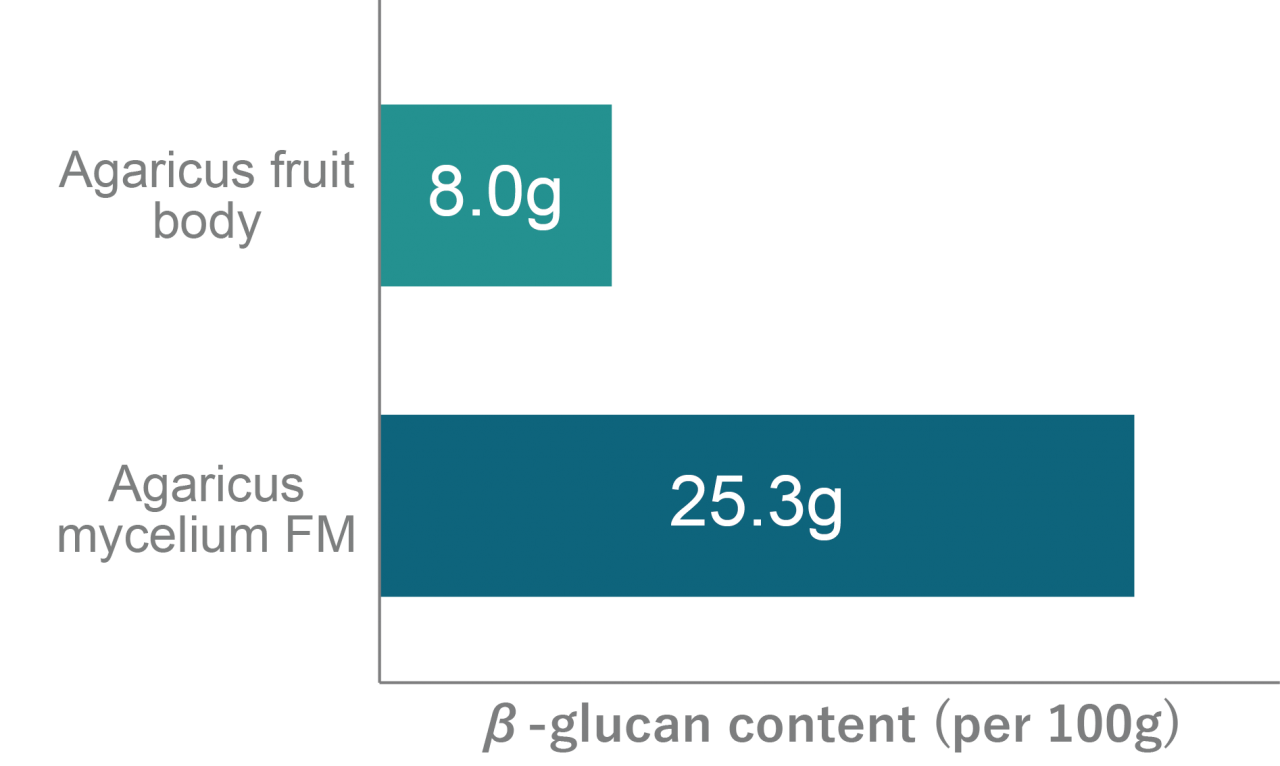
Using our unique cultivation technology Agaricus mycelium is cultivated in large quantities to further be purified, dried, sterilised and ground into final product powder state. Agaricus mycelium FM has been investigated to contain less carbohydrate and energy and more dietary fibre than Agaricus fruit body. It has also been confirmed that the amount of immunostimulant component β-glucan is more than three times higher than that of the Agaricus fruit bodies.
2. Added Functionality
- 2-1 Innate Immune Activation (Tumor Cell Suppression)
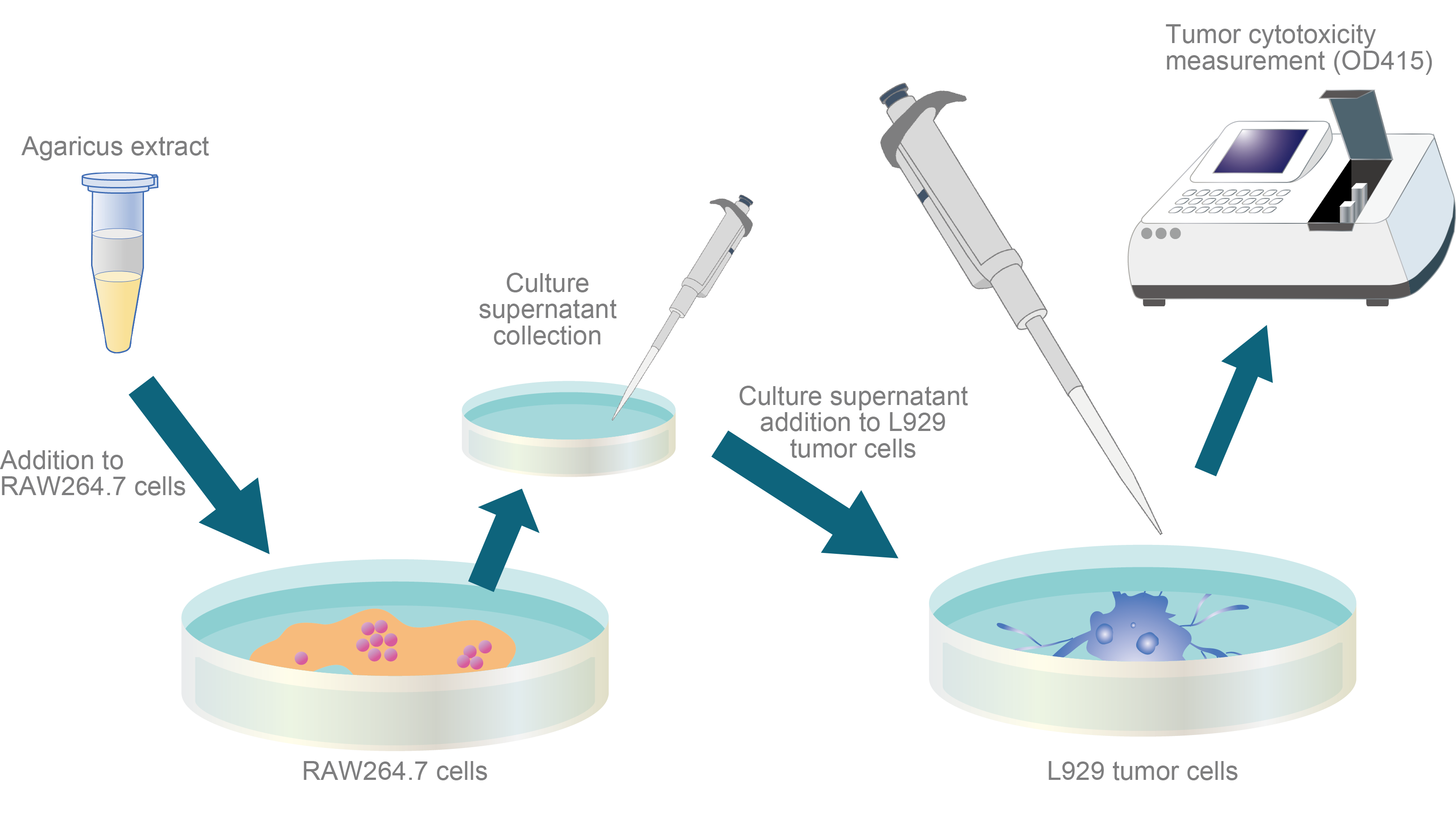
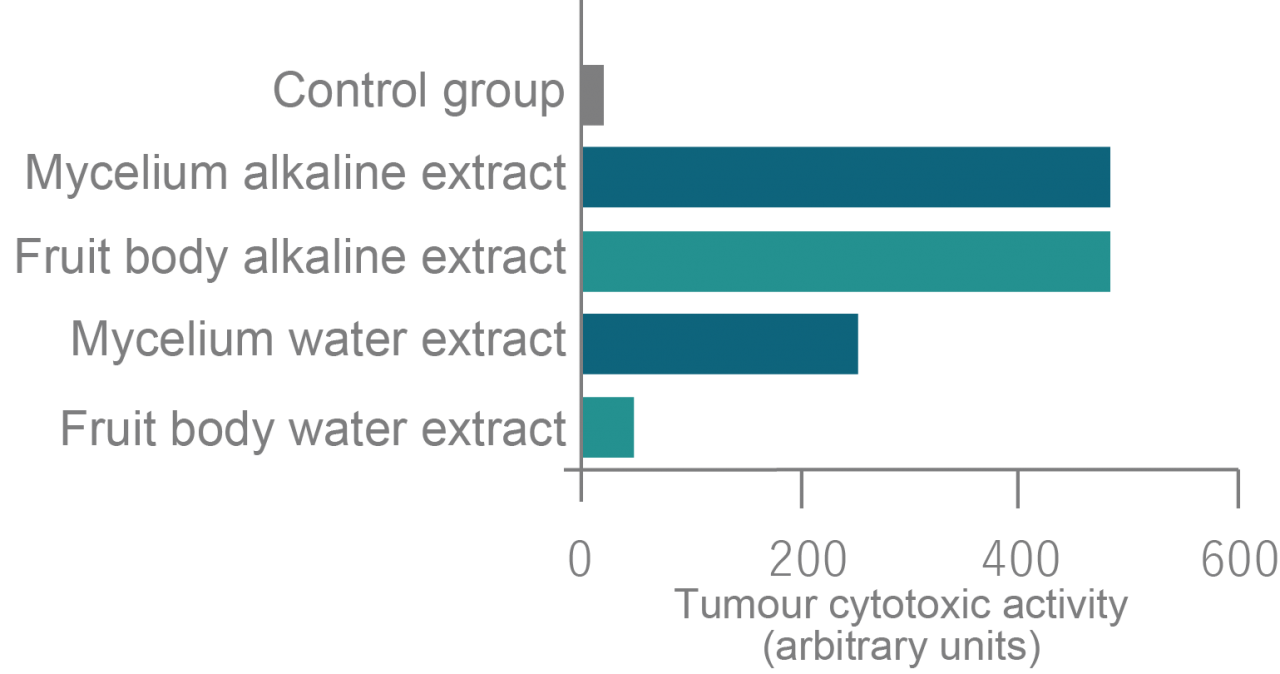
Trial Outline
The tumour cell-damaging activity of macrophage cells caused by the addition of Agaricus extract was investigated. A macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7) was supplemented with 500 µg/mL of either Agaricus fruit body or Agaricus mycelium extracts. The culture medium supernatant was added to L929 tumour cells, which are cancer-forming fibroblasts of mouse origin, to assess their disabling activity on tumour cells.
Trial Results
Addition of Agaricus mycelium and Agaricus fruit body alkaline extracts showed high tumor cytotoxicity. In comparison, an Agaricus mycelium extract in hot water showed about half the tumor cytotoxic activity of the alkaline one, whilst fruit body hot water extract showed almost none.
- 2-2 Acqured Immune Activation (Increased Lymphocyte Proliferative)
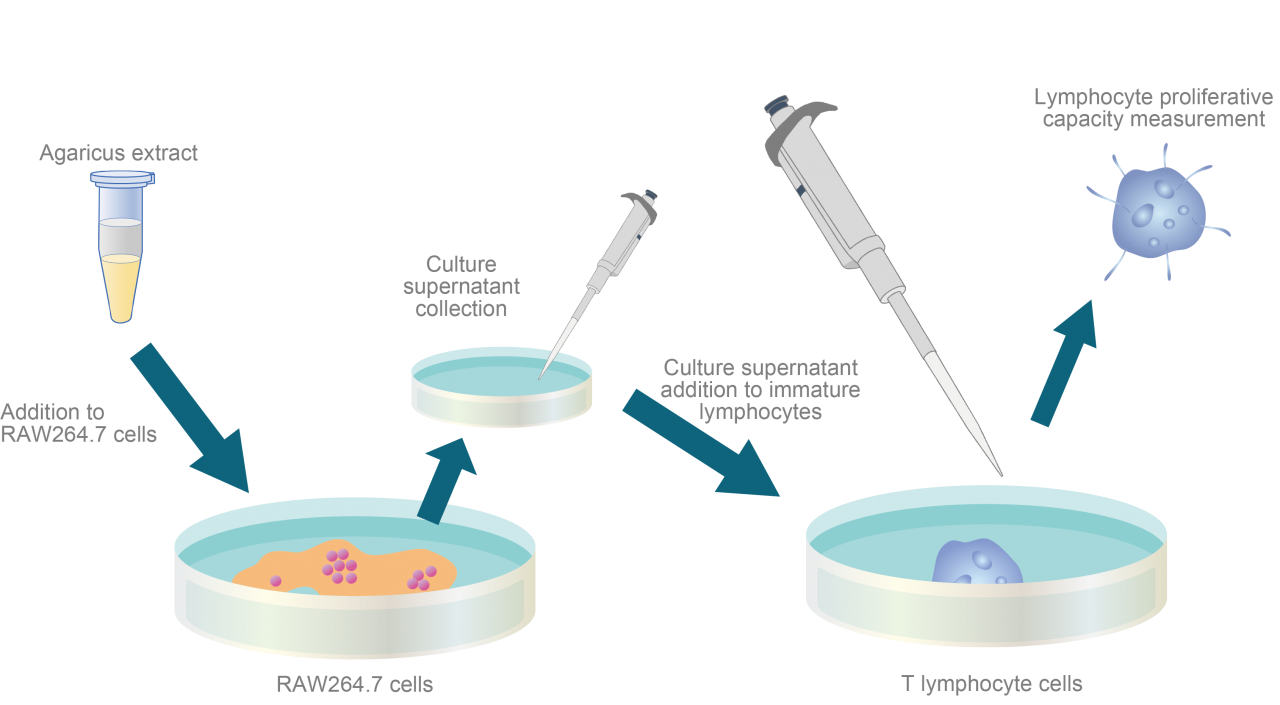
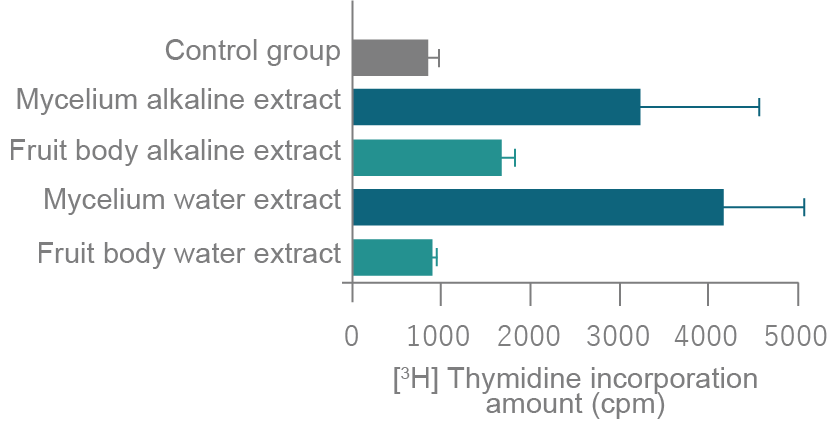
Trial Outline
Agaricus extracts effect on the proliferative activity of lymphocyte cells by macrophages was investigated. A macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7) was supplemented with 500 µg/mL of either Agaricus fruit body or Agaricus mycelium extracts. The culture supernatant was added to the medium of immature thymocyte lymphocyte cells taken from C3H/HeJ mice. Proliferative potential of the lymphocyte cells was assessed by the uptake of [methyl-3H]thymidine added to the medium into the lymphocyte cells.
Trial Results
Both alkaline and water extracts of Agaricus mycelium were found to incorporate more [methyl-3H]thymidine than these from the Agaricus fruit body. This indicates that the Agaricus mycelium extract induced lymphocyte proliferation by activating macrophages to produce lymphocyte growth factors.
- 2-3 Lymphocyte Proliferation Effect in Mice
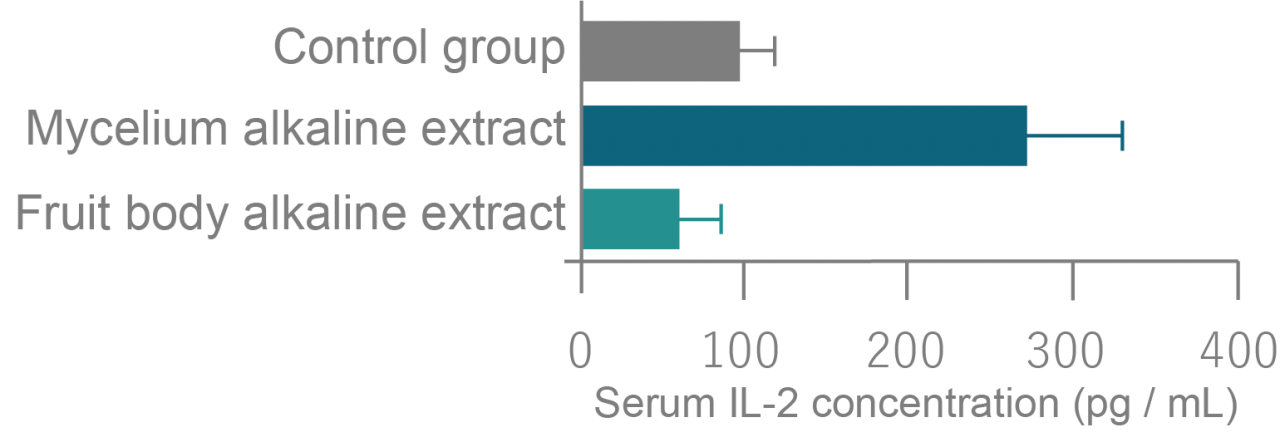
Trial Outline
To investigate in vivo effects of Agaricus Mycelium FM, mice were treated with alkaline extracts of both Agaricus mycelium and fruit bodies for four weeks. The concentration of the lymphocyte growth factor cytokine IL-2 in the serum was measured by ELISA method afterwards.
| Subjects | 5-week-old female C3H/HeJ mice |
| Samples | Agaricus alkaline extract (100 mg/kg B.W) |
| Period | 28 days (intragastric administration every 3 days) |
| Trial outline | Mice kept in an SPF environment were administered approximately with 2 mg/0.2 mL of alkaline Agaricus extract suspended in saline solution via gastric sonde once every three days for 28 days. |
Trial Results
The addition of alkaline extract of Agaricus mycelium was found to induce high serum IL-2 production.
(3rd Int Conf of Mushroom Biology and Mushroom Products, 1999)
